The Federal Reserve seems to be creeping nearer to an final result that its personal workers economists seen as unlikely simply six months in the past: reducing inflation again to a standard vary with out plunging the financial system right into a recession.
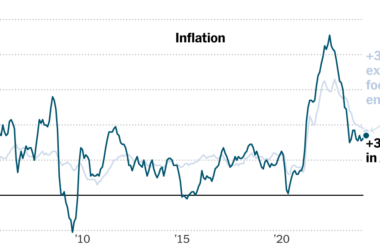
Loads might nonetheless go flawed. However inflation has come down notably in current months — it’s working at 3.1 p.c on a yearly foundation, down from a 9.1 p.c peak in 2022. On the similar time, progress is stable, customers are spending, and employers proceed to rent.
That mixture has come as a shock to economists. Many had predicted that cooling a red-hot job market with much more job openings than accessible staff would be a painful course of. As an alternative, staff returned from the labor market sidelines to fill open spots, serving to alongside a comparatively painless rebalancing. On the similar time, therapeutic provide chains have helped to spice up inventories and ease shortages. Items costs have stopped pushing inflation greater, and have even begun to tug it down.
The Fed is hoping for “a continuation of what now we have seen, which is the labor market coming into higher stability with out a vital enhance in unemployment, inflation coming down with out a vital enhance in unemployment, and progress moderating with out a vital enhance in unemployment,” Jerome H. Powell, the Fed chair, mentioned Wednesday.
As Fed policymakers look forward to 2024, they’re aiming squarely for a delicate touchdown: Officers are attempting to evaluate how lengthy they should preserve rates of interest excessive to make sure that inflation is totally underneath management with out grinding financial progress to an unnecessarily painful halt. That maneuver is prone to be a fragile one, which is why Mr. Powell has been cautious to keep away from declaring victory prematurely.
However policymakers clearly see it coming into view, based mostly on their financial projections. The Fed chair signaled on Wednesday that charges had been unlikely to rise from their 5.25 to five.5 p.c setting except inflation levels a shocking resurgence, and central bankers predicted three price cuts by the top of 2024 as inflation continues to chill and joblessness rises solely barely.
If they will nail that touchdown, Mr. Powell and his colleagues could have achieved an infinite feat in American central banking. Fed officers have traditionally tipped the financial system right into a recession when attempting to chill inflation from heights like these it reached in 2022. And after a number of years throughout which Mr. Powell has faced criticism for failing to anticipate how lasting and critical inflation would grow to be, so successful could be prone to form his legacy.
“The Fed proper now appears fairly dang good, when it comes to how issues are turning out,” mentioned Michael Gapen, head of U.S. Economics at Financial institution of America.
Respondents in a survey of market members carried out recurrently by the analysis agency MacroPolicy Views are extra optimistic in regards to the odds of a delicate touchdown than ever earlier than: 74 p.c mentioned that no recession was wanted to decrease inflation again to the Fed’s goal in a Dec. 1-7 survey, up from a low of 41 p.c in September 2022.
Fed workers members began to anticipate a recession after a number of banks blew up early this 12 months, however stopped forecasting one in July.
Individuals had been glum in regards to the prospects for a mild touchdown partly as a result of they thought the Fed had been late to react to speedy inflation. Mr. Powell and his colleagues argued all through 2021 that greater costs had been prone to be “transitory,” at the same time as some distinguished macroeconomists warned that it’d final.
The Fed was compelled to vary course drastically as these warnings proved prescient: Inflation has now been above 2 p.c for 33 straight months.
As soon as central bankers began elevating rates of interest in response, they did so quickly, pushing them from near-zero initially of 2022 to their present vary of 5.25 to five.5 p.c by July of this 12 months. Many economists fearful that slamming the brakes on the financial system so abruptly would trigger whiplash within the type of a recession.
However the transitory name is trying considerably higher now — “transitory” simply took a very long time to play out.
A lot of the explanation inflation has moderated comes right down to the therapeutic of provide chains, easing of shortages in key items like automobiles, and a return to one thing that appears extra like prepandemic spending developments through which households are shopping for a variety of products and companies as an alternative of simply stay-at-home splurges like couches and train gear.
Briefly, the pandemic issues that the Fed had anticipated to show short-term did fade. It simply took years quite than months.
“As a constitution member of group transitory, it took rather a lot longer than many people thought,” mentioned Richard Clarida, the previous Fed vice chair who served till early 2022. However, he famous, issues have adjusted.
Fed insurance policies have performed a task in cooling demand and protecting customers from adjusting their expectations for future inflation, so “the Fed does deserves some credit score” for that slowdown.
Whereas greater rates of interest didn’t heal provide chains or persuade customers to cease shopping for so many sweatpants, they’ve helped to chill the marketplace for key purchases like housing and automobiles considerably. With out these greater borrowing prices, the financial system might need grown much more strongly — giving corporations the wherewithal to lift costs extra drastically.
Now, the query is whether or not inflation will proceed to chill even because the financial system hums alongside at a stable clip, or whether or not it should take a extra marked financial slowdown to drive it down the remainder of the way in which. The Fed itself expects progress to gradual considerably subsequent 12 months, to 1.4 p.c from 2.6 p.c this 12 months, based mostly on recent projections.
“Definitely they’ve carried out very properly, and higher than I had anticipated,” mentioned William English, a former senior Fed economist who’s now a professor at Yale. “The query stays: Will inflation come all the way in which again to 2 p.c with out extra slack within the labor and items markets than we’ve seen to date?”
Thus far, the job market has proven little signal of cracking. Hiring and wage progress have slowed, however unemployment stood at a traditionally low 3.7 p.c in November. Customers proceed to spend, and progress within the third quarter was unexpectedly sizzling.
Whereas these are optimistic developments, they preserve alive the chance that the financial system could have slightly an excessive amount of vim for inflation to chill fully, particularly in key companies classes.
“We don’t know the way lengthy it should take to go the final mile with inflation,” mentioned Karen Dynan, a former Treasury chief economist who teaches at Harvard.
Provided that, setting coverage subsequent 12 months might show to be extra of an artwork than a science: If progress is cooling and inflation is coming down, slicing charges might be a reasonably apparent selection. However what if progress is robust? What if inflation progress stalls however progress collapses?
Mr. Powell acknowledged a few of that uncertainty this week.
“Inflation retains coming down, the labor market retains getting again into stability,” he mentioned. “It’s to date, so good, though we sort of assume that it’s going to get tougher from right here, however to date, it hasn’t.”
Mr. Powell, a lawyer by coaching who spent a bit of his profession in non-public fairness, isn’t an economist and has at instances expressed warning about utilizing key financial fashions and guides too religiously. That lack of devotion to the fashions could turn out to be useful over the following 12 months, Mr. Gapen of Financial institution of America mentioned.
It might go away the Fed chief — and the establishment he leads — extra versatile as they react to an financial system that has been devilishly difficult to foretell as a result of, within the wake of the pandemic, previous expertise is proving to be a poor precedent.
“Possibly it was proper to have a man who was skeptical of frameworks handle the ship through the Covid interval,” Mr. Gapen mentioned.