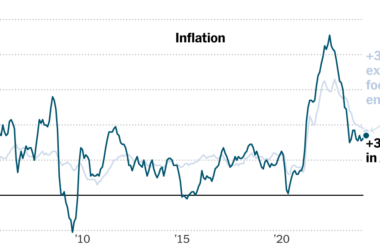
With inflation falling, unemployment low and the Federal Reserve signaling it may quickly start chopping rates of interest, forecasters have gotten more and more optimistic that the U.S. financial system may keep away from a recession.
Wells Fargo final week grew to become the newest large financial institution to foretell that the financial system will obtain a smooth touchdown, gently slowing quite than screeching to a halt. The financial institution’s economists had been forecasting a recession for the reason that center of 2022.
But if forecasters had been flawed after they predicted a recession final 12 months, they might be flawed once more, this time in the wrong way. The dangers that economists highlighted in 2023 haven’t gone away, and up to date financial information, although nonetheless largely constructive, has recommended some cracks beneath the floor.
Certainly, on the identical day that Wells Fargo reversed its recession name, its economists additionally revealed a report pointing to indicators of weak point within the labor market. Hiring has slowed, they famous, and only a handful of industries account for a lot of the current job features. Layoffs stay low, however employees who do lose their jobs are having a more durable time discovering a brand new one.
“We’re not out of the woods but,” mentioned Sarah Home, an writer of the report. “We nonetheless assume that recession threat continues to be elevated.”
Ms. Home and different economists have harassed that there are good causes for his or her current optimism. The financial system has weathered the speedy rise in rates of interest significantly better than most forecasters anticipated. And the surprisingly brisk slowdown in inflation has given policymakers extra leeway — if unemployment begins to rise, for instance, the Fed may lower charges to attempt to extend the restoration.
If a recession does arrive, economists say there are three predominant ways in which may occur:
1. The Delayed Slowdown
The principle motive that economists predicted a recession final 12 months is that they anticipated the Fed to trigger one.
Fed officers spent the final two years making an attempt to rein in inflation by elevating rates of interest on the quickest tempo in many years. The purpose was to tamp down demand simply sufficient to carry down inflation, however not a lot that corporations would start widespread layoffs. Most forecasters — together with many contained in the central financial institution — thought that such a cautious calibration would show too tough and that after shoppers and companies started to tug again, a recession was all however inevitable.
It’s nonetheless potential that their evaluation was proper and that solely the timing was flawed. It takes time for the consequences of upper rates of interest to stream by way of the financial system, and there are causes that course of could also be slower than normal this time.
Many corporations, for instance, refinanced their debt throughout the interval of ultralow rates of interest in 2020 and 2021; solely when they should refinance once more will they really feel the chew of upper borrowing prices. Many households had been capable of shrug off greater charges as a result of they’d constructed up financial savings or paid off money owed earlier within the pandemic.
These buffers are eroding, nonetheless. The additional financial savings are dwindling or already gone, in accordance with most estimates, and bank card borrowing is setting data. Larger mortgage charges have slowed the housing market. Scholar mortgage funds, which had been paused for years throughout the pandemic, have resumed. State and native governments are chopping their budgets as federal assist dries up and tax income falls.
“If you take a look at all of the helps that customers have had, a variety of these are fading,” mentioned Dana M. Peterson, chief economist for the Convention Board.
The manufacturing and housing sectors have already skilled recessions, with output contracting, Ms. Peterson mentioned, and enterprise funding is lagging extra broadly. Customers are the ultimate pillar holding up the restoration. If the job market weakens even just a little, she added, “that may wake individuals up and get them to assume, ‘Nicely, I could not get fired however I would get fired, and a minimum of I’m not going to get that large bonus,” and scale back their spending accordingly.
2. The Return of Inflation
The largest motive economists have turn out to be extra optimistic about the opportunity of a smooth touchdown is the speedy cooling of inflation. By some shorter-term measures, inflation is now barely above the Fed’s long-run goal of two %; costs for some bodily items, corresponding to furnishings and used automobiles, are literally falling.
If inflation is underneath management, that provides policymakers extra room to maneuver, permitting them to chop rates of interest if unemployment begins to rise, for instance. Already, Fed officers have indicated they anticipate to start chopping charges someday this 12 months to maintain the restoration on monitor.
But when inflation picks up once more, policymakers may discover themselves in a decent spot, unable to chop charges if the financial system loses momentum. Or worse, they might even be pressured to think about elevating charges once more.
“Regardless of the robust demand, we’ve nonetheless had inflation coming down,” mentioned Raghuram Rajan, an economist on the College of Chicago Sales space College of Enterprise who has held prime positions on the Worldwide Financial Fund and the Financial institution of India. “The query now could be, going ahead, are we going to be so fortunate?”
Inflation fell in 2023 partly as a result of the provision aspect of the financial system improved considerably: Provide chains returned largely to regular after the disruptions attributable to the pandemic. The financial system additionally acquired an inflow of employees as immigration rebounded and People returned to the job market. That meant corporations may get the supplies and labor they wanted to satisfy demand with out elevating costs as a lot.
Few individuals anticipate the same provide resurgence in 2024, nonetheless. That implies that for inflation to maintain falling, it could require a slowdown in demand. That might be very true within the service sector, the place costs are typically extra tightly tied to wages — and the place wage progress has remained comparatively robust due to the demand for employees.
Monetary markets may be making the Fed’s job harder. The inventory and bond markets each rallied late final 12 months, which may successfully cancel out among the Fed’s efforts by making traders really feel richer and permitting companies to borrow extra cheaply. That would assist the financial system within the brief time period, however pressure the Fed to behave extra aggressively, elevating the danger that it’ll trigger a recession down the highway.
“If we don’t keep sufficiently tight monetary circumstances, there’s a threat that inflation will choose again up and reverse the progress we’ve made,” Lorie Ok. Logan, the president of the Federal Reserve Financial institution of Dallas, warned this month in a speech at an annual convention for economists in San Antonio. Because of this, she mentioned, the Fed ought to depart open the opportunity of one other improve in rates of interest.
3. The Unwelcome Shock
The financial system caught some fortunate breaks final 12 months. China’s weak restoration helped hold commodity costs in examine, which contributed to the slowdown in U.S. inflation. Congress averted a authorities shutdown and resolved a debt-ceiling standoff with comparatively little drama. The breakout of struggle within the Center East had solely a modest impact on international oil costs.
There is no such thing as a assure that luck will proceed in 2024. The widening struggle within the Center East is disrupting delivery lanes within the Crimson Sea. Congress will face one other government-funding deadline in March after passing a stopgap spending invoice on Thursday. And new threats may emerge: a extra lethal coronavirus pressure, battle within the Taiwan Strait, a disaster in some beforehand obscure nook of the monetary system.
Any of these prospects may upset the stability that the Fed is making an attempt to strike by inflicting a spike in inflation or a collapse in demand — or each directly.
“That’s the factor that, in case you’re a central banker, retains you up at night time,” mentioned Karen Dynan, a Harvard economist and former official within the Treasury Division.
Though such dangers all the time exist, the Fed has little margin for error. The financial system has slowed considerably, leaving much less of a buffer within the occasion of an extra hit to progress. However with inflation nonetheless elevated — and recollections of excessive inflation nonetheless contemporary — the Fed may have a tough time ignoring even a brief spike in costs.
“There’s room for a mistake on each side that may find yourself creating job loss,” Ms. Dynan mentioned. “The dangers are extra balanced, definitely, than they had been a 12 months in the past, however I don’t assume that’s offering that rather more consolation to the choice makers.”
Audio produced by Patricia Sulbarán.